Fiber optic cable design has a major impact on how well a network performs, especially in outdoor environments where moisture, shifting temperatures, and mechanical stress are constant concerns. Among the many cable constructions available today, the gel-filled loose tube design is one of the most trusted choices for rugged outdoor installations. Known for its durability and resistance to harsh conditions, it remains a preferred solution for long-distance and high-capacity fiber networks.
This guide explains what gel-filled loose tube cables are, how they’re built, where they’re used, and how they compare to other designs—along with practical tips for installation.
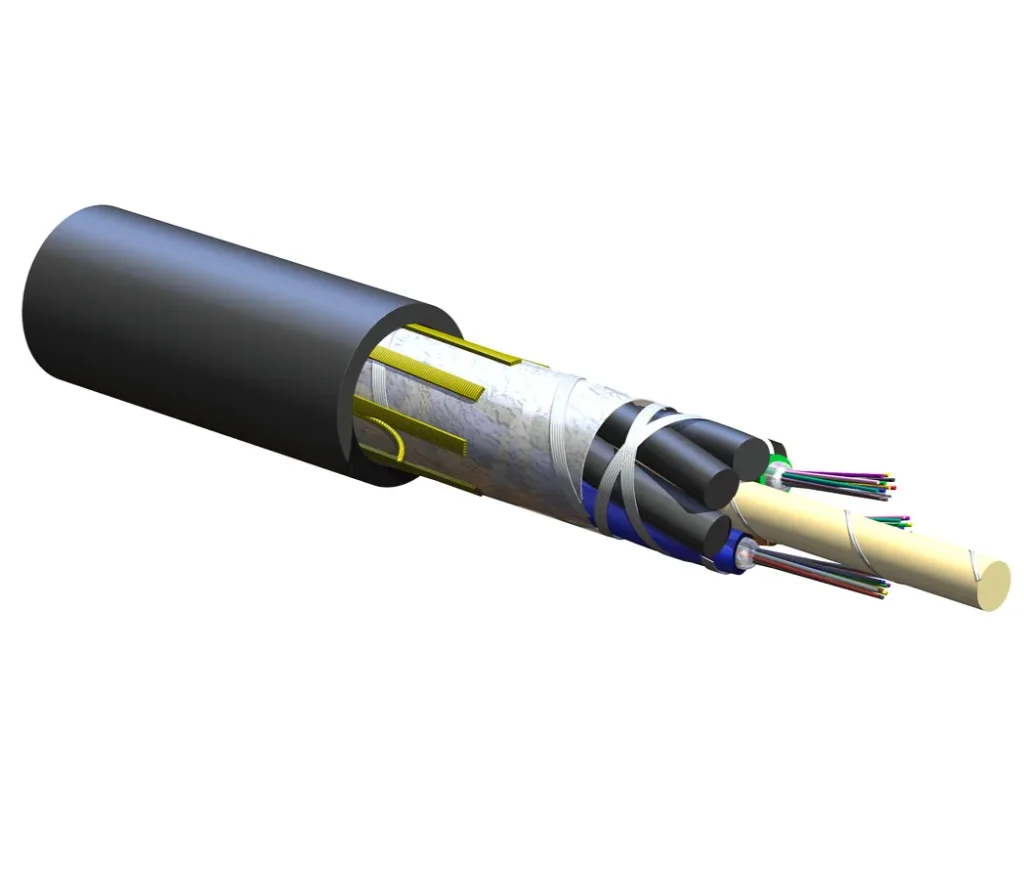
What Is a Gel-Filled Loose Tube Fiber Cable?
A gel-filled loose tube cable houses multiple optical fibers inside small buffer tubes that contain a water-blocking gel. Because the fibers are not tightly bound, they can move slightly within the tube, protecting them from environmental stress. The gel prevents moisture from entering or spreading inside the cable, making the design particularly useful in outdoor, underground, and high-humidity environments.
How These Cables Are Constructed
The structure of a gel-filled loose tube cable typically includes:
- Optical fibers for data transmission
- Loose buffer tubes containing the fibers and gel
- Water-blocking gel that shields fibers from moisture and shock
- Central strength member (steel or fiberglass) to maintain structure
- Aramid yarn or similar reinforcement for tensile strength
- Inner sheath to protect internal components
- Optional metallic or dielectric armor for rodent resistance or extra strength
- Outer jacket made from UV-resistant materials such as polyethylene
Each layer serves a specific purpose, contributing to the cable’s ability to perform well in challenging environments.
Key Advantages of Gel-Filled Loose Tube Cables
1. Excellent Moisture Protection
The gel prevents water from spreading through the buffer tubes, even if the outer jacket is damaged. This makes the cable ideal for buried installations, damp climates, and underwater pathways.
2. Strong Temperature Resistance
Because the fibers can move freely within the tubes, they experience less stress during temperature fluctuations. This flexibility helps maintain long-term performance across extreme heat or cold.
3. Added Mechanical Cushioning
The gel absorbs vibration and shock, reducing the chance of fiber breaks during installation or environmental movement such as soil shifting.
4. High Fiber Density
Loose tube designs can accommodate large fiber counts, making them suitable for network backbones and long-haul communication systems.
5. Ideal for Long-Distance Runs
The protective structure reduces attenuation and maintains signal integrity, which is valuable for long-route and high-capacity networks.
Common Applications
Gel-filled loose tube cables are widely used in outdoor and industrial environments, including:
- Telecommunications backbones
- Direct-burial and duct installations
- FTTH distribution networks
- Rail and highway infrastructure
- Campus interbuilding connections
- Harsh-weather outdoor routing
Their ability to withstand moisture and mechanical stress makes them a reliable option in areas exposed to the elements.
Potential Drawbacks and Challenges
1. Messy Termination
The gel must be cleaned off completely before splicing or terminating, which requires more time and materials.
2. More Installation Prep
Compared to gel-free designs, these cables take longer to prepare and handle during field work.
3. Not Suitable Indoors
Most gel-filled cables do not meet indoor fire-rating requirements and should be transitioned to indoor-rated cables before entering buildings.
4. Environmental Concerns
Petroleum-based gels must be handled carefully and disposed of properly to avoid contamination.
Tips for Installer Success
- Have proper cleaning tools and solvents ready before opening buffer tubes.
- Keep splice areas clean and allow extra time for preparation.
- Document fiber layouts carefully, especially in high-fiber-count cables.
- Schedule installation during dry conditions when possible.
- Provide training for technicians unfamiliar with gel-filled designs.
These steps help streamline installation and ensure optimal cable performance.
Relevant Standards to Check
Quality gel-filled cables typically follow:
- ITU-T G.652 / G.657 fiber performance standards
- Telcordia GR-20 cable durability requirements
- IEC 60794 environmental and mechanical testing protocols
- RoHS compliance for safe materials
Always confirm that the cable you select meets the specifications required for your project.
Final Thoughts
Gel-filled loose tube fiber optic cables offer a dependable solution for outdoor and high-moisture environments. Their moisture resistance, durability, and high-capacity design make them ideal for long-term installations exposed to the elements. While these cables require more preparation and care during installation, their long-lasting performance often outweighs the added effort.
Choosing between gel-filled and dry-blocked alternatives ultimately depends on the environment, maintenance expectations, and project design. With proper planning and handling, gel-filled loose tube cables can deliver decades of reliable performance in demanding field conditions.